宏基因組二、三代測序混合組裝軟件OPERA-MS
混合組裝宏基因組實現高精度分析人體微生物組中的抗性基因和移動元件
Hybrid metagenomic assembly enables high-resolution analysis of resistance determinants and mobile elements in human microbiomes
Nature Biotechnology [IF:31.864]
2019-07-29 Articles
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0191-2
第一作者:Denis Bertrand1
通訊作者:Niranjan Nagarajan1,7*
其它作者:Jim Shaw, Manesh Kalathiyappan, Amanda Hui Qi Ng, M. Senthil Kumar, Chenhao Li(李陳浩), Mirta Dvornicic, Janja Paliska Soldo, Jia Yu Koh, Chengxuan Tong, Oon Tek Ng, Timothy Barkham, Barnaby Young, Kalisvar Marimuthu, Kern Rei Chng, Mile Sikic
作者單位:
1 計算與系統生物學,新加坡基因組所(Computational & Systems Biology, Genome Institute of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore)
7 新加坡國立大學(National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore.)
熱心腸日報
Nature子刊:宏基因組二、三代混合組裝新軟件OPERA-MS
創作:劉永鑫 審核:劉永鑫 08月02日
原標題:混合宏基因組組裝實現人體微生物組中的抗性基因和移動元件的高精度分析
-
OPERA-MS采用重複感知聚類和精確的支架方法結合,實現二、三代序列的混合宏基因組組裝;
-
基于模擬和真實宏基因組樣本評估,獲得目前最高質量的宏基因組,比長讀長更高的堿基准確度,比短讀長更高的連續性和比混合組裝更少的錯誤,可獲得低豐度物種的高質量基因組;
-
軟件還可實現同一物種內菌株水平組裝,獲得稀有物種的高質量參考基因組;
-
結合納米孔讀長,實現80個完整質粒或噬菌體序列組裝,爲研究腸道抗生素抗性組精細研究提供可能。
二代測序通量高、准確度高,但讀長短;三代測序讀長長,但錯誤率高、成本高。將這兩者的優勢結合,目前在宏基因組領域還沒有得到廣泛應用,存在很多技術難題沒有解決。近日,來自新加坡基因組所的Niranjan Nagarajan課題組發布了一款二、三代測序混合組裝軟件OPERA-MS,組裝結果不僅堿基准確率高,而且短讀長數據拼接長度提升了一個數量級。
OPERA-MS整合了宏基因組聚類和精確支架算法,基于虛擬腸道微生物組和人工群落數據測序,研究者僅用9×長讀長覆蓋深度組裝出了接近目前最完整的宏基因組,也組裝出低豐度(<1%)物種的高質量基因組。值得一提的是,OPERA-MS還可在亞種水平上獲得基因組結果。將Nanopore測序應用于抗生素治療病人的腸道宏基因組研究,發現長讀長組裝質量較短讀長提升了200倍。這一重鎊成果于7月29日發表于世界頂級期刊《Nature Biotechnology》。
摘要
通過高通量宏基因組測序已經實現了微生物組的組成分析。然而,現有方法不是設計用于組裝來自短讀長和長讀長混合序列。我們提出了一個名爲OPERA-MS的混合宏基因組組裝軟件,它將組裝宏基因組采用重複感知聚類和精確的支架方法結合,實現精確地組裝複雜群落。使用預定義的體外和虛擬腸道微生物組進行評估,OPERA-MS組裝的宏基因組具有比長讀長(> 5×; Canu)更高的堿基對准確度,比短讀長更高的連續性(~10× NGA50; MEGAHIT,IDBA-UD) ,metaSPAdes)和比非宏基因組混合組裝軟件(2×; hybridSPAdes)更少的組裝錯誤。OPERA-MS在同一物種的多個基因組存在下提供菌株分辨率的組裝結果,可在~9倍長讀取覆蓋率下獲得稀有物種的高質量參考基因組(<1%)。我們使用OPERA-MS組裝28個抗生素治療患者的腸道宏基因組,並顯示包含長納米孔讀長産生更多連續組裝(比短讀長組裝提高200倍),包括超過80個成環質粒或噬菌體序列和一個新的263 kbp巨型噬菌體。高質量的混合組軟件可以對人類患者的腸道抗生素抗性組進行精細的觀察。
Characterization of microbiomes has been enabled by high-throughput metagenomic sequencing. However, existing methods are not designed to combine reads from short- and long-read technologies. We present a hybrid metagenomic assembler named OPERA-MS that integrates assembly-based metagenome clustering with repeat-aware, exact scaffolding to accurately assemble complex communities. Evaluation using defined in vitro and virtual gut microbiomes revealed that OPERA-MS assembles metagenomes with greater base pair accuracy than long-read (>5×; Canu), higher contiguity than short-read (~10× NGA50; MEGAHIT, IDBA-UD, metaSPAdes) and fewer assembly errors than non-metagenomic hybrid assemblers (2×; hybridSPAdes). OPERA-MS provides strain-resolved assembly in the presence of multiple genomes of the same species, high-quality reference genomes for rare species (<1%) with ~9× long-read coverage and near-complete genomes with higher coverage. We used OPERA-MS to assemble 28 gut metagenomes of antibiotic-treated patients, and showed that the inclusion of long nanopore reads produces more contiguous assemblies (200× improvement over short-read assemblies), including more than 80 closed plasmid or phage sequences and a new 263 kbp jumbo phage. High-quality hybrid assemblies enable an exquisitely detailed view of the gut resistome in human patients.
主要結果
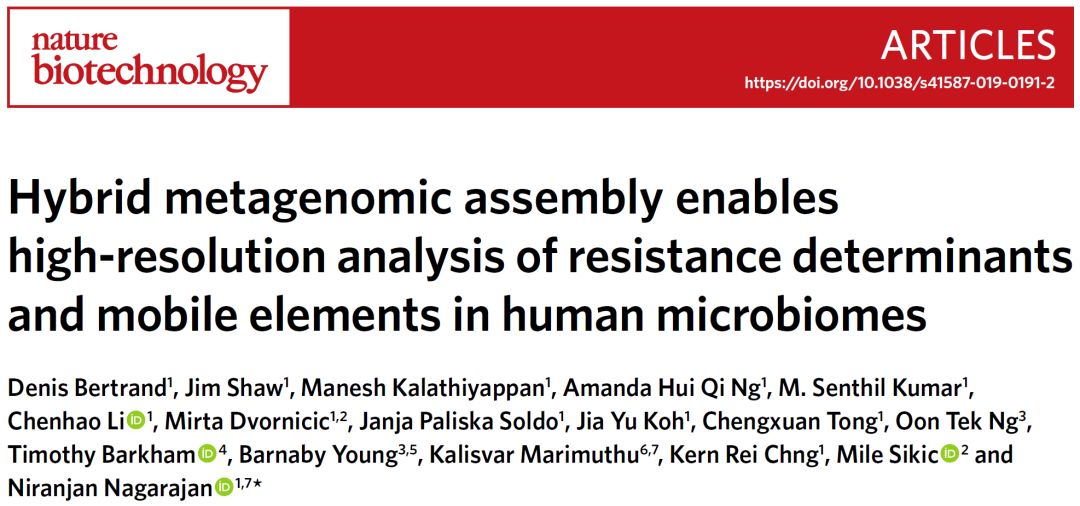
圖1. OPERA-MS工作流程圖
Fig. 1: OPERA-MS workflow.
首先將宏基因組的短讀長拼接爲重疊群,並將短讀取和長讀長比對至重疊群以獲得覆蓋信息和跨越序列(步驟1)。然後綁定跨越讀長獲得組裝圖中重疊群之間的邊,該組裝圖表示整個宏基因組的連續性信息(步驟2)。將重疊群組織成層次聚類,其中重疊群之間的距離隨基因組距離及其覆蓋差異而增加(步驟3)。然後基于BIC(貝葉斯信息准則)將樹切割成最佳簇(步驟4)。可選步驟,爲了改善可獲得參考基因組物種的聚類,計算每個聚類與完整細菌基因組數據庫之間的Mash基因組距離(步驟5)。然後,如果在裝配圖中存在支持信息以形成物種特定的超級簇,則合並簇(步驟6)。進一步分析這些超級簇以解卷積來自可區分的亞種基因組的重疊群(步驟7)。最後,使用針對分離基因組的程序(OPERA-LG;步驟8),獨立地構建每個簇並填充間隙。
Short reads are first assembled by a metagenomic assembler into contigs, and short and long reads are mapped to them to obtain coverage information and spanning reads (Step 1). Spanning reads are then bundled to get edges between contigs for an assembly graph that represents the contiguity information of the whole metagenome (Step 2). Contigs are organized into a hierarchical clustering where the distance between contigs increases with genomic distance and their difference in coverage (Step 3). The tree is then cut into optimal clusters based on the BIC (Step 4). Optionally, to improve the clustering for species where a reference genome is available, the Mash genomic distance between each cluster and a database of complete bacterial genomes is computed (Step 5). Clusters are then merged if there is supporting information in the assembly graph to form species-specific super-clusters (Step 6). These super-clusters are further analyzed to deconvolute contigs that come from distinguishable subspecies genomes (Step 7). Finally, each cluster is independently scaffolded and gap-filled using a program meant for isolate genomes (OPERA-LG; Step 8).
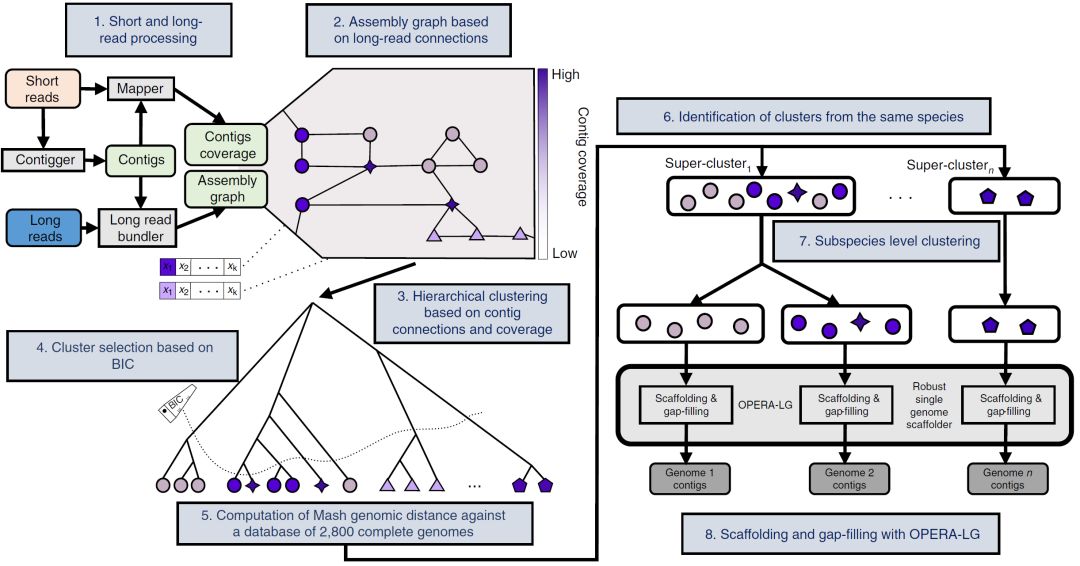
圖2. 宏基因組數據混合組裝基因組評測
Fig. 2: Benchmarking hybrid assembly of genomes from metagenomes.
a-c,作爲短讀長代表性組裝軟件metaSPAdes(a),長讀長組裝軟件Canu(b)和混合組裝軟件OPERA-MS(c)的測序覆蓋率增加與組裝連續性的增加。請注意,混合裝配在跨越覆蓋方面有效改進了短讀長和長讀長的裝配結果,可在低至9×長讀長覆蓋度下産生接近完整的基因組(NGA50 > 1 Mbp)。未組裝的基因組顯示爲帶有黑色邊框的圓圈。d,OPERA-MS與其他組裝軟件相比較提高的裝配連續性(NGA50)。對于MEGAHIT和IDBA-UD,組裝基因組中覆蓋度上升的數量爲3,12,20和19,對于metaSPAdes和hybridSPAdes爲3,13,21和19,對于Canu爲4和16。請注意,Canu不會組裝低覆蓋率的基因組,因此在這些範圍內不提供指標。數據以箱形圖表示(中心線,中位數;箱限,上下四分位數; 須線,1.5×四分位數間距; 點,異常值)。e,不同組裝軟件的組裝錯誤率,實線表示中值。除了hybridSPAdes之外,大多數組裝軟件每 Mbp(虛線)産生大約1個錯誤的組裝。在每個部分中,每個數據點代表來自模擬群落的一個基因組。
a–c, Increase in assembly contiguity as a function of read coverage for a representative short-read assembler (a), long-read assembler (b) and hybrid assembler (c). Note that hybrid assembly improves over short- and long-read assembly in terms of scaling across coverage ranges and producing near-complete genomes (NGA50 >1 Mbp) with as little as 9× long-read coverage. Unassembled genomes are shown as circles with black borders. d, Improvements in assembly contiguity (NGA50) provided by OPERA-MS in comparison with other assemblers as a function of long-read coverage. The number of assembled genomes, in ascending order of coverage is 3, 12, 20 and 19 for MEGAHIT and IDBA-UD, 3, 13, 21 and 19 for metaSPAdes and hybridSPAdes and 4 and 16 for Canu. Note that Canu does not assemble low-coverage genomes and hence metrics are not provided in those ranges. Data are presented as box plots (center line, median; box limits, upper and lower quartiles; whiskers, 1.5× interquartile range; points, outliers). e, Misassembly rates for different assemblers, with solid lines indicating median values. Most assemblers produce ~1 large misassembly per Mbp (dashed line), except for hybridSPAdes. In each part, each data point represents one genome from the mock communities.
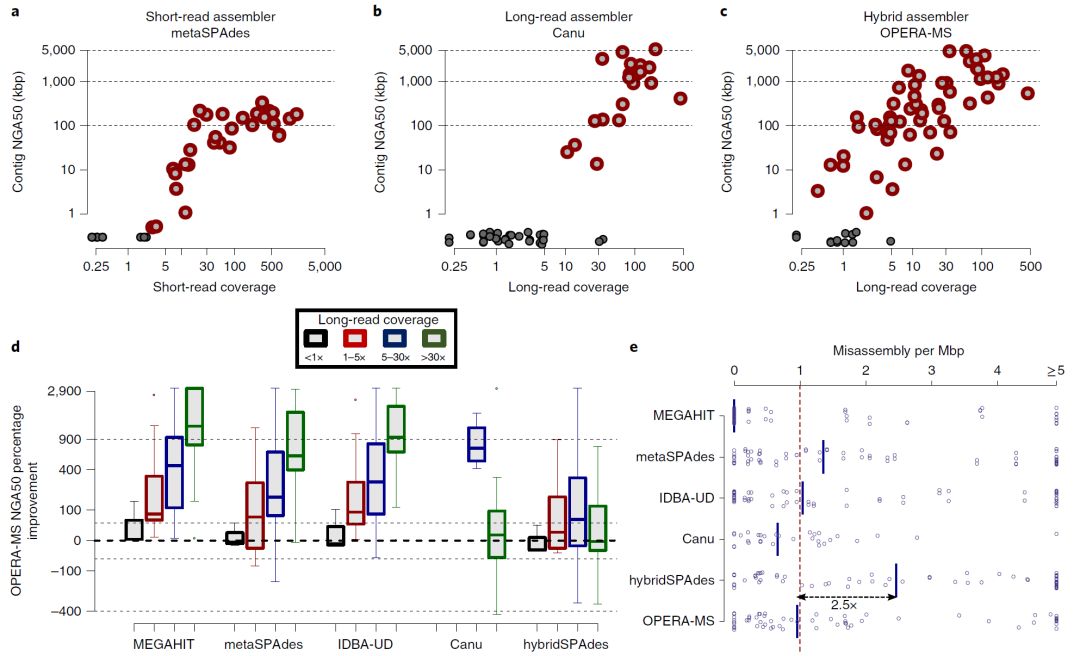
圖3. 組裝虛擬腸道微生物組
Fig. 3: Assembly of a virtual gut microbiome.
a,構建虛擬腸道微生物組,代表複雜的宏基因組數據集,同時保留評估組裝與金標准參考的能力。
b,與不同覆蓋範圍內的其他組裝軟件相比,使用OPERA-MS獲得組裝連續性(NGA50)的改進情況。點代表在宏基因組中具有至少兩個菌株的物種(在GIS20和S2中存在的物種,如MetaPhlAn2報道的豐度 > 0.1%(參考文獻49)(v.2.6.0))。按照覆蓋度的上升,組裝的基因組的數量對于Canu是1,對于其他方法是2,6,4和5個。數據以箱形圖表示(中心線,中位數;箱限,上下四分位數; 須線,1.5×四分位數間距; 點,異常值)。
c,不同組裝軟件的組裝錯誤率(每個基因組一個點)的比較,實線表示中值。
d,在分箱後評估僅Illumina數據(M,MEGAHIT)和混合(H,hybridSPAdes; O,OPERA-MS)組裝宏基因組組裝以用于下遊分析。包含最大部分參考基因組的區域(GIS20參考文獻;具有粗體名稱的物種在宏基因組中具有至少兩個菌株)評估以下參數:(1)基因組完整性,在分箱中基因組的比例,(2)基因組純度,分箱中堿基對應正確參考的百分比,(3)基因完整性,在分箱中完全組裝的基因比例和(4)通路完整性,其組成基因超過90%的通路出現在組裝的分箱中。
a, Construction of a virtual gut microbiome that represents a complex metagenomic data set while retaining the ability to evaluate assemblies against gold-standard references. b, Improvement in assembly contiguity (NGA50) obtained using OPERA-MS compared with other assemblers over different coverage ranges. Dots represent species that have at least two strains in the metagenome (species present in GIS20 and S2 with an abundance >0.1% as reported by MetaPhlAn2 (ref. 49) (v.2.6.0)). The number of assembled genomes, in ascending order of coverage, was 1 for Canu and 2, 6, 4 and 5 for the other methods. Data are presented as box plots (center line, median; box limits, upper and lower quartiles; whiskers, 1.5× interquartile range; points, outliers). c, Comparison of misassembly rates (one dot per genome) for different assemblers, with solid lines indicating median values. d, Evaluation of Illumina-only (M, MEGAHIT) and hybrid (H, hybridSPAdes; O, OPERA-MS) metagenomic assemblies after binning for their utility in downstream analysis. Bins that contained the largest fraction of a reference genome (GIS20 references; species with bold names have at least two strains in the metagenome) were evaluated for (1) genome completeness, the fraction of the genome represented in the bin, (2) genome purity, percentage of bases in the bin that correspond to the correct reference, (3) gene completeness, fraction of genes that were fully assembled in the bin and (4) pathway completeness, fraction of pathways with over 90% of their constituent genes being assembled and binned together.
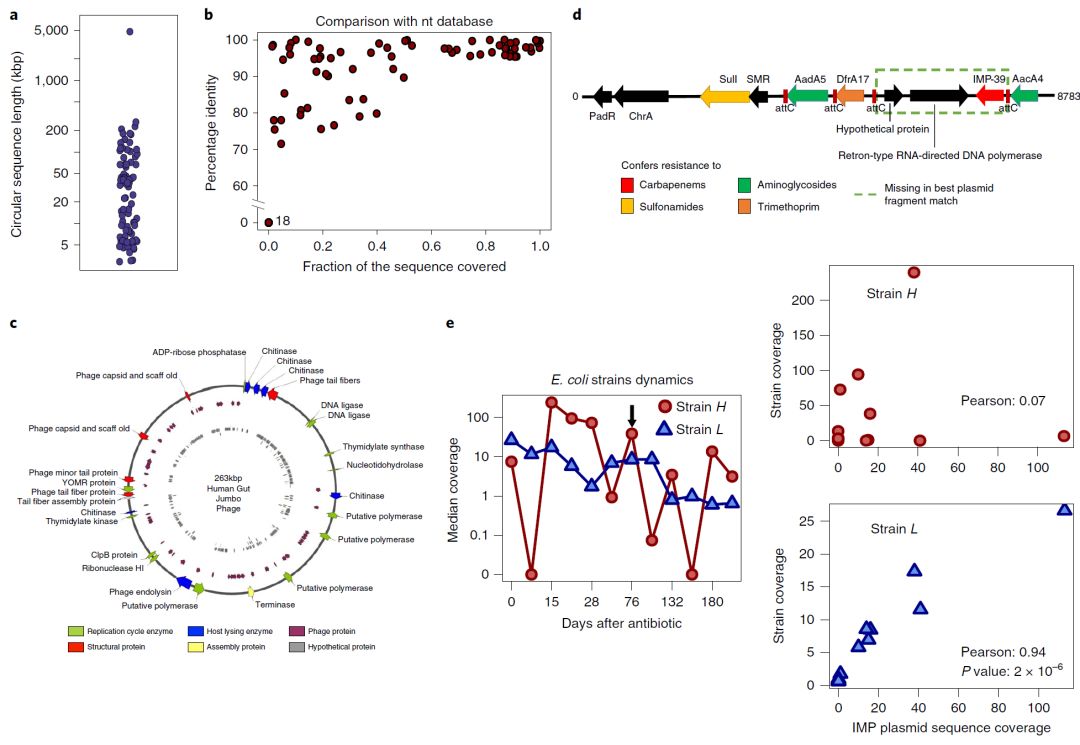
圖4. 移動元件和與人腸道微生物組中宿主物種的關聯
Fig. 4: Mobile elements and association with host species in the human gut microbiome.
a,來自OPERA-MS的28個人腸道宏基因組數據集中完全組裝成環序列的基因組大小分布,說明了組裝不同大小和複雜性的環狀基因組的能力(質粒,噬菌體和細菌基因組)。
b,與NCBI核苷酸(nt)數據庫中的序列(基于BLAST搜索)比對,覆蓋序列的比例與組裝的環狀序列的平均序列相似度。許多組裝序列從端到端(右上角)顯示出與已知序列的良好比對和相似度,但是一些僅具有局部相似性(左上角),並且一些似乎是新的(左下角; 18個序列) 。
c,觀察到最大的新(在nt數據庫中沒有匹配)環狀序列(263kbp)的注釋,發現與噬菌體生命周期相關的蛋白,包括複制、組裝和宿主裂解相關,表明組裝的序列是假定的巨型噬菌體。
d,OPERA-MS從耐受碳青黴烯的腸杆菌科細菌定植患者的腸道微生物組中組裝出新的多重抗性區域。除臨床相關的碳青黴烯酶基因區域外,該區域還含有賦予氨基糖苷類、甲氧苄氨嘧啶和磺胺類抗性的基因,限制了治療選擇。
e,OPERA-MS菌株水平組裝可以進行質粒與基因組基于跨越時間點的測序覆蓋信息進行關聯(n = 12)。左圖:來自第76天的數據的雜合宏基因組裝配中觀察到的兩種大腸杆菌菌株基因組的覆蓋度的變化(黑色箭頭)。右圖:質粒覆蓋度與兩種大腸杆菌菌株之間的相關性表明它是可能含有IMP基因的質粒的菌株L使用R中的學生t-檢驗(雙側)計算P值。
a, Distribution of genomes sizes for fully assembled circular sequences from OPERA-MS in 28 human gut metagenome data sets, illustrating the ability to assemble circular genomes of varying sizes and complexity (plasmids, phages and bacterial genomes). b, Fraction of sequence covered versus average sequence identity of the assembled circular sequences in comparison to sequences in the NCBI nucleotide (nt) database (based on BLAST searches). Many of the assembled sequences showed good alignment and homology to known sequences from end to end (top right corner), but some only had local similarities (top left corner), and a few appear to be new (bottom left corner; 18 sequences). c, Annotation of the largest (263 kbp) observed new circular sequence (no matches in nt database) revealed proteins associated with a phage life cycle, including replication, assembly and host lysis, indicating that the assembled sequence is a putative jumbo phage. d, A new multiple resistance region assembled by OPERA-MS from the gut microbiome of a patient colonized by carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Apart from the clinically relevant carbapenemase gene cassette, the region also harbors genes that confer resistance to aminoglycosides, trimethoprim and sulfonamides, limiting treatment options. e, Strain level assembly with OPERA-MS enabled association of plasmid to genome based on correlation in read coverage across timepoints (n = 12). Left panel: Variation in coverage of two Escherichia coli strain genomes seen in the hybrid metagenomic assembly of data from day 76 (black arrow). Right panel: Correlation between the coverage of the plasmid and the two E. coli strains reveals that it is strain L that likely harbors the IMP gene containing plasmid. The P value was computed using Student’s t-test in R (two-sided).
總結
本文介紹了一種基于混合數據的宏基因組組裝軟件OPERA-MS,比較分析了其與其他幾種短讀長、長讀長數據組裝軟件對宏基因組研究的效能。它能夠顯著的提升組裝的連續性,並且還能夠解決亞種級基因組的組裝,解決了長讀長數據的原始錯誤率、覆蓋度問題和短讀長數據的讀長缺陷,即使對于低深度覆蓋的數據也能有出色的表現。爲了驗證軟件的應用能力,研究者還模擬了人體腸道微生物組的數據,發現其對于臨床宏基因組、抗生素耐藥性基因的研究上面也能提供較好的幫助。
Reference
-
Denis Bertrand, Jim Shaw, Manesh Kalathiyappan, Amanda Hui Qi Ng, M. Senthil Kumar, Chenhao Li, Mirta Dvornicic, Janja Paliska Soldo, Jia Yu Koh, Chengxuan Tong, Oon Tek Ng, Timothy Barkham, Barnaby Young, Kalisvar Marimuthu, Kern Rei Chng, Mile Sikic, and Niranjan Nagarajan. (2019). Hybrid metagenomic assembly enables high-resolution analysis of resistance determinants and mobile elements in human microbiomes. Nature Biotechnology.10.1038/s41587-019-0191-2
-
有了OPERA-MS,人體腸道微生物不用愁!
相關閱讀
-
NBT:宏基因組”讀雲”10X建庫+雅典娜算法組裝獲得微生物高質量基因組
猜你喜歡
10000+:菌群分析 寶寶與貓狗 梅毒狂想曲 提DNA發Nature Cell專刊 腸道指揮大腦
系列教程:微生物組入門 Biostar 微生物組 宏基因組
專業技能:學術圖表 高分文章 生信寶典 不可或缺的人
一文讀懂:宏基因組 寄生蟲益處 進化樹
必備技能:提問 搜索 Endnote
文獻閱讀 熱心腸 SemanticScholar Geenmedical
擴增子分析:圖表解讀 分析流程 統計繪圖
16S功能預測 PICRUSt FAPROTAX Bugbase Tax4Fun
在線工具:16S預測培養基 生信繪圖
科研經驗:雲筆記 雲協作 公衆號
編程模板: Shell R Perl
生物科普: 腸道細菌 人體上的生命 生命大躍進 細胞暗戰 人體奧秘
寫在後面
爲鼓勵讀者交流、快速解決科研困難,我們建立了“宏基因組”專業討論群,目前己有國內外5000+ 一線科研人員加入。參與討論,獲得專業解答,歡迎分享此文至朋友圈,並掃碼加主編好友帶你入群,務必備注“姓名-單位-研究方向-職稱/年級”。PI請明示身份,另有海內外微生物相關PI群供大佬合作交流。技術問題尋求幫助,首先閱讀《如何優雅的提問》學習解決問題思路,仍未解決群內討論,問題不私聊,幫助同行。
學習16S擴增子、宏基因組科研思路和分析實戰,關注“宏基因組”